header
The header field is part of the Block and UncleBlock structures. It contains metadata that summarizes and secures the block's contents, and it plays a critical role in consensus and chain validation.
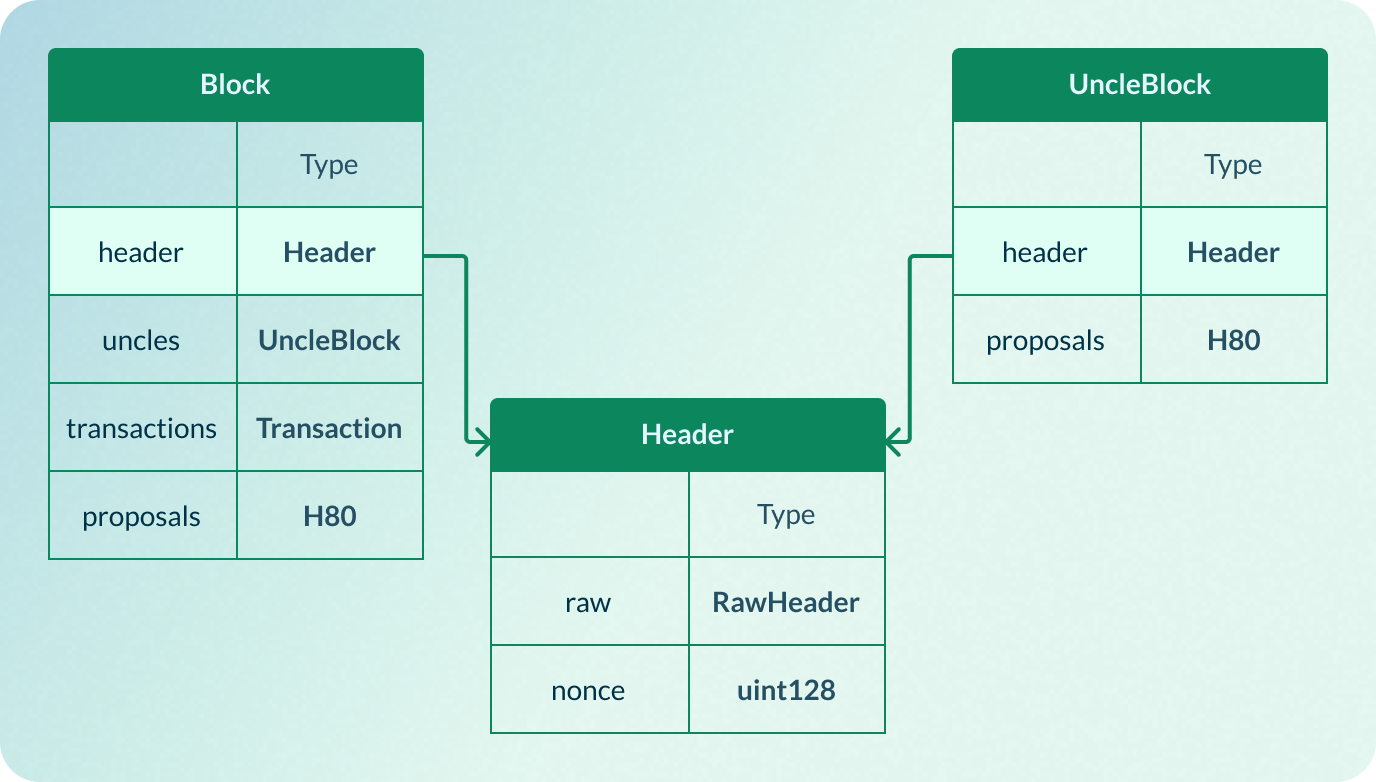
Structure of Header
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
raw | RawHeader | The payload of the block header. |
nonce | uint128 | The solution of the PoW puzzle. Similar to Bitcoin nonce. |
RawHeader
RawHeader is the payload of the block header.
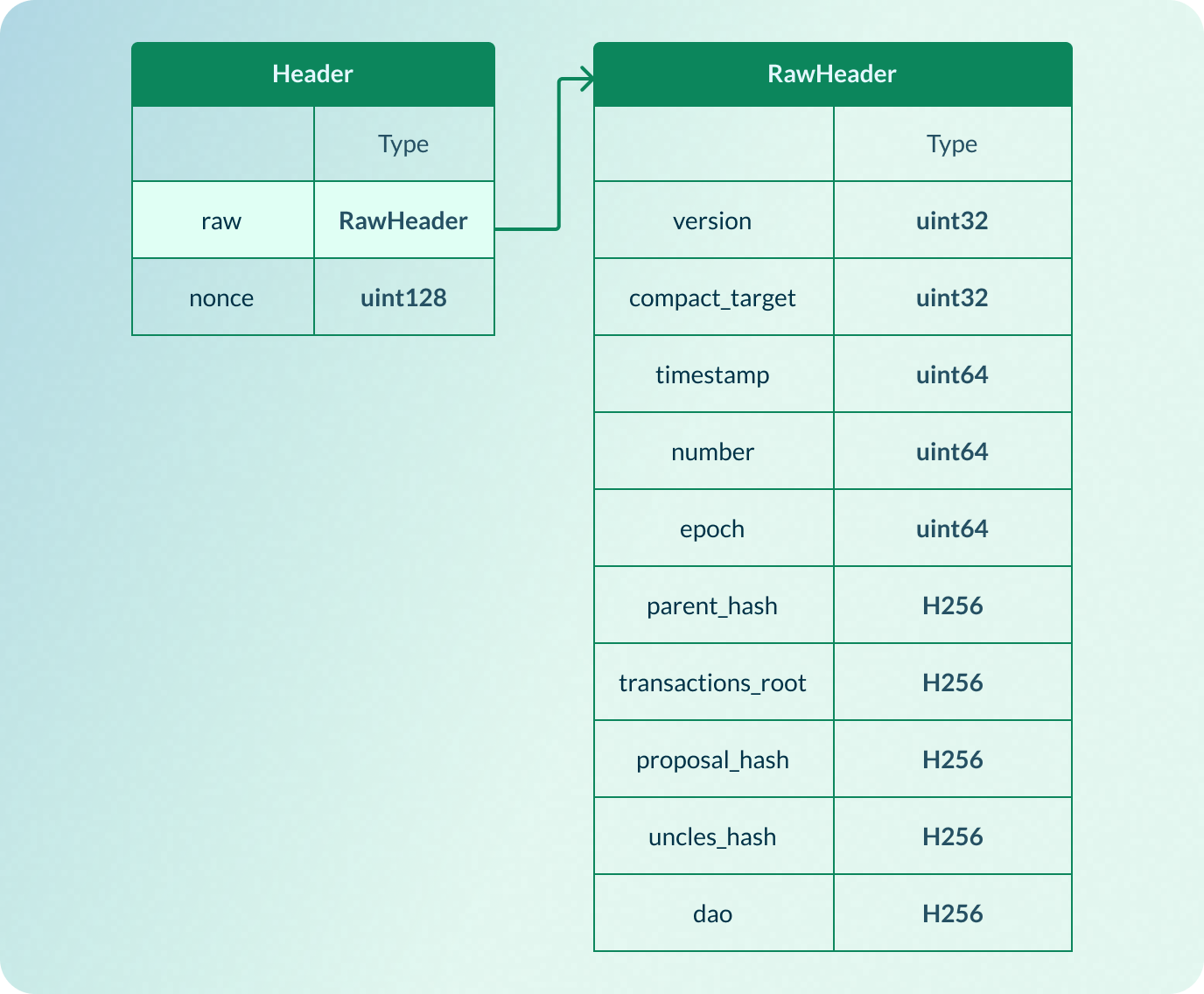
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
version | Uint32 | Version of the block, used to address potential compatibility issues that might arise after a fork |
compact_target | Uint32 | PoW difficulty represented in compact target format |
timestamp | Uint64 | A Unix time timestamp in milliseconds |
number | Uint64 | Indicates block height |
epoch | Uint64 | Information of the current epoch. Assuming number represents the current epoch number, index represents the index of the block in the current epoch (starting at 0), and length represents the length of the current epoch, the value must be (number & 0xFFFFFF) | ((index & 0xFFFF) << 24) | ((length & 0xFFFF) << 40) |
parent_hash | H256 (hash) | Hash of the parent block |
transactions_root | H256 (hash) | A hash obtained by concatenating the CBMT (Complete Binary Merkle Tree) root of the transaction hashes and the CBMT root of the transaction witness hashes |
proposals_hash | H256 (hash) | Hash of the concatenated proposal IDs. Defaults to all zeros if no proposals exist. |
uncles_hash | H256 (hash) | Hash of the concatenated hashes of uncle block headers. Defaults to all zeros if no proposals exist. |
dao | Bytes | Contains DAO-related data. Refer to RFC0023: Deposit and Withdraw in Nervos DAO for details. |
nonce | Uint128 | The solution of the PoW puzzle. Similar to Bitcoin nonce. |
Refer to the RawHeader in RFC-0027 for an in-depth explanation.
Verification Process for Header
This following snippet describes the process to validate the PoW for a block header in the Nervos CKB blockchain:
- Serializing and hashing the block's raw data.
- Concatenating the hash with the nonce.
- Running the concatenated result through the Eaglesong algorithm.
- (Optional) Re-hashing for the Testnet.
- Converting the final output to an integer and ensuring it meets the required difficulty target.
pow_hash := ckbhash(molecule_serialize(raw))
pow_message := pow_hash || to_le(nounce)
pow_output := eaglesong(pow_message)
// for Testnet, there is another round of hash
// pow_output = ckbhash(pow_output)
from_be(pow_output) <= compact_to_target(raw.compact_target)
Functions used in the pseudocode
:=: assignment||: binary concatenationckbhash: Blake2b hash with CKB specific configurationto_le: converts unsigned integer to bytes in little-endian. The bytes count is the same with the integer width.from_be: converts bytes encoded in big-endian to an unsigned integermolecule_serialize: serializes a structure into binary using its schemaeaglesong: CKB’s Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm. See RFC0010: Eaglesongcompact_to_target: restores the target from its compact form, which is the difficulty target encoded byraw.compact_target
Header Hash Derivation & Usage
The header is hashed to produce a unique header_hash. This header_hash is then used to reference the block.
header_hash := ckb_hash(molecule_serialize(header))